Calculator using python 🤩
We have made a calculator using python language.
We can calculate easily on that calculator.
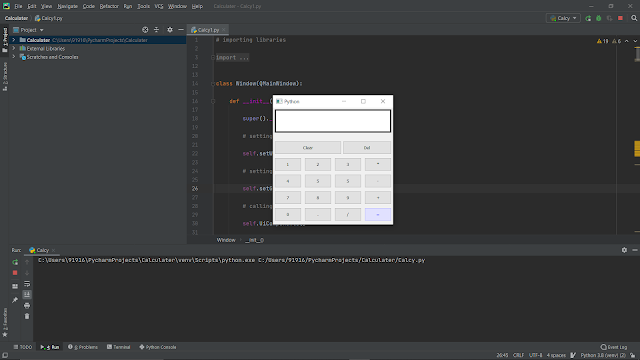
Here's are the code for the Calculator
# importing libraries from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui from PyQt5.QtGui import * from PyQt5.QtCore import * import sys class Window(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() # setting title self.setWindowTitle("Python ") # setting geometry self.setGeometry(100, 100, 360, 350) # calling method self.UiComponents() # showing all the widgets self.show() # method for widgets def UiComponents(self): # creating a label self.label = QLabel(self) # setting geometry to the label self.label.setGeometry(5, 5, 350, 70) # creating label multi line self.label.setWordWrap(True) # setting style sheet to the label self.label.setStyleSheet("QLabel" "{" "border : 4px solid black;" "background : white;" "}") # setting alignment to the label self.label.setAlignment(Qt.AlignRight) # setting font self.label.setFont(QFont('Arial', 15)) # adding number button to the screen # creating a push button push1 = QPushButton("1", self) # setting geometry push1.setGeometry(5, 150, 80, 40) # creating a push button push2 = QPushButton("2", self) # setting geometry push2.setGeometry(95, 150, 80, 40) # creating a push button push3 = QPushButton("3", self) # setting geometry push3.setGeometry(185, 150, 80, 40) # creating a push button push4 = QPushButton("4", self) # setting geometry push4.setGeometry(5, 200, 80, 40) # creating a push button push5 = QPushButton("5", self) # setting geometry push5.setGeometry(95, 200, 80, 40) # creating a push button push6 = QPushButton("5", self) # setting geometry push6.setGeometry(185, 200, 80, 40) # creating a push button push7 = QPushButton("7", self) # setting geometry push7.setGeometry(5, 250, 80, 40) # creating a push button push8 = QPushButton("8", self) # setting geometry push8.setGeometry(95, 250, 80, 40) # creating a push button push9 = QPushButton("9", self) # setting geometry push9.setGeometry(185, 250, 80, 40) # creating a push button push0 = QPushButton("0", self) # setting geometry push0.setGeometry(5, 300, 80, 40) # adding operator push button # creating push button push_equal = QPushButton("=", self) # setting geometry push_equal.setGeometry(275, 300, 80, 40) # adding equal button a color effect c_effect = QGraphicsColorizeEffect() c_effect.setColor(Qt.blue) push_equal.setGraphicsEffect(c_effect) # creating push button push_plus = QPushButton("+", self) # setting geometry push_plus.setGeometry(275, 250, 80, 40) # creating push button push_minus = QPushButton("-", self) # setting geometry push_minus.setGeometry(275, 200, 80, 40) # creating push button push_mul = QPushButton("*", self) # setting geometry push_mul.setGeometry(275, 150, 80, 40) # creating push button push_div = QPushButton("/", self) # setting geometry push_div.setGeometry(185, 300, 80, 40) # creating push button push_point = QPushButton(".", self) # setting geometry push_point.setGeometry(95, 300, 80, 40) # clear button push_clear = QPushButton("Clear", self) push_clear.setGeometry(5, 100, 200, 40) # del one character button push_del = QPushButton("Del", self) push_del.setGeometry(210, 100, 145, 40) # adding action to each of the button push_minus.clicked.connect(self.action_minus) push_equal.clicked.connect(self.action_equal) push0.clicked.connect(self.action0) push1.clicked.connect(self.action1) push2.clicked.connect(self.action2) push3.clicked.connect(self.action3) push4.clicked.connect(self.action4) push5.clicked.connect(self.action5) push6.clicked.connect(self.action6) push7.clicked.connect(self.action7) push8.clicked.connect(self.action8) push9.clicked.connect(self.action9) push_div.clicked.connect(self.action_div) push_mul.clicked.connect(self.action_mul) push_plus.clicked.connect(self.action_plus) push_point.clicked.connect(self.action_point) push_clear.clicked.connect(self.action_clear) push_del.clicked.connect(self.action_del) def action_equal(self): # get the label text equation = self.label.text() try: # getting the ans ans = eval(equation) # setting text to the label self.label.setText(str(ans)) except: # setting text to the label self.label.setText("Wrong Input") def action_plus(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + " + ") def action_minus(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + " - ") def action_div(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + " / ") def action_mul(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + " * ") def action_point(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + ".") def action0(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "0") def action1(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "1") def action2(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "2") def action3(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "3") def action4(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "4") def action5(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "5") def action6(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "6") def action7(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "7") def action8(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "8") def action9(self): # appending label text text = self.label.text() self.label.setText(text + "9") def action_clear(self): # clearing the label text self.label.setText("") def action_del(self): # clearing a single digit text = self.label.text() print(text[:len(text) - 1]) self.label.setText(text[:len(text) - 1]) # create pyqt5 app App = QApplication(sys.argv) # create the instance of our Window window = Window() # start the app sys.exit(App.exec())
Here's the video for the example and idea.

2 Comments
Click here for CommentsWe provide Classroom training on IBM Certified Data Science at Hyderabad for the individuals who believe hand-held training. We teach as per the Indian Standard Time (IST) with In-depth practical Knowledge on each topic in classroom training, 80 – 90 Hrs of Real-time practical training classes. There are different slots available on weekends or weekdays according to your choices. We are also available over the call or mail or direct interaction with the trainer for active learning.
ReplyFor any queries feel free to Call/WhatsApp us on +91-9951666670 or mail at info@innomatics.in
data
science training in hyderabad
Data Science Course in Hyderabad
Incredibly conventional blog and articles. I am realy very happy to visit your blog. Directly I am found which I truly need. Thankful to you and keeping it together for your new post.
Replydata analytics training in yelahanka
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon